Are We Over-Cleaning Our Skin?
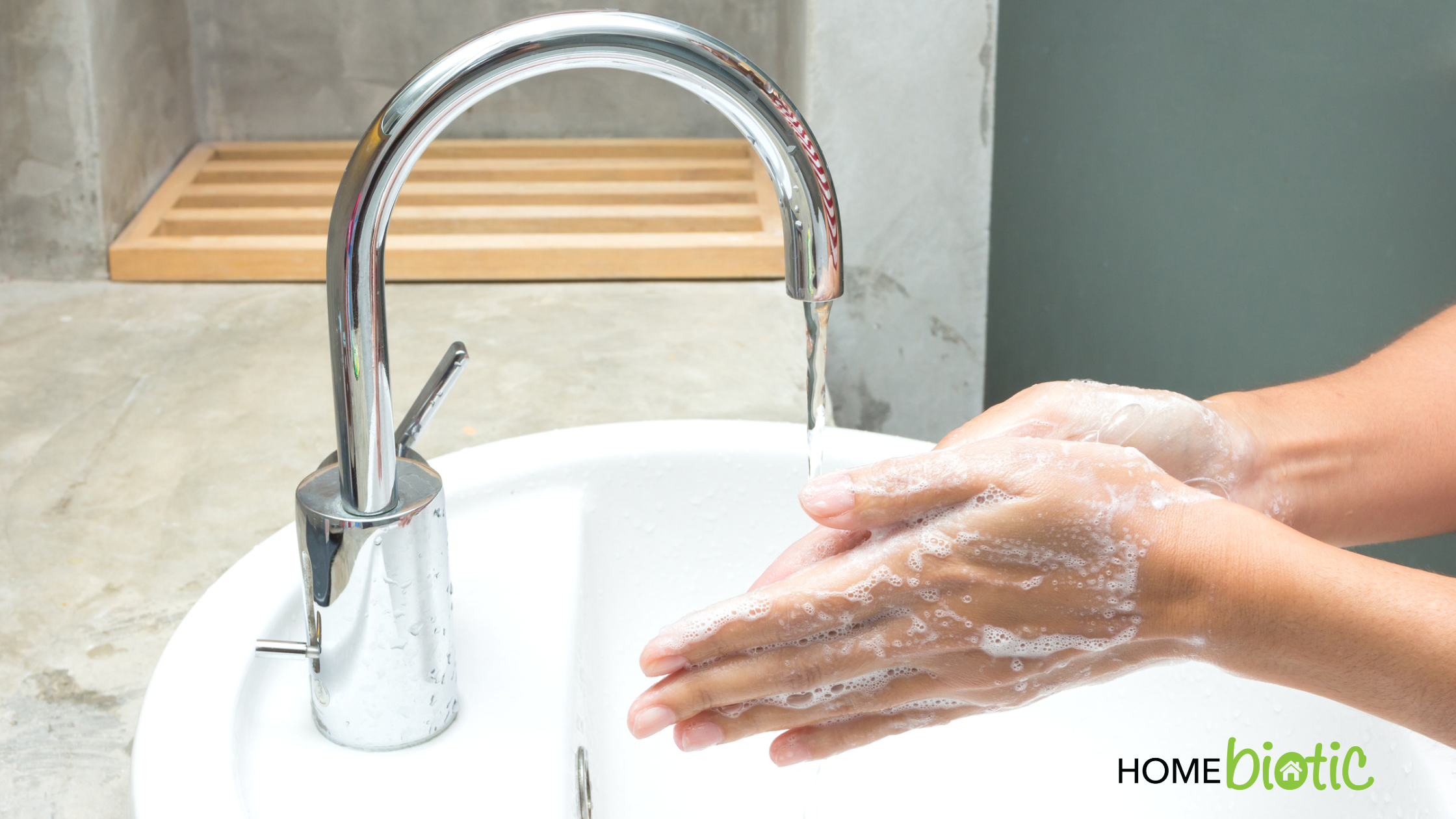

In these current times, the topic of under and over-cleaning our skin and home environment is discussed more than ever. There have always been debates about how often we should clean and which soaps or cleansers to choose. But with the pandemic, everyone is more concerned and possibly more confused as well.
 Undoubtedly, in the past several months, there’s been a steady stream of antibacterial and alcohol-based soaps being marketed to the general public. And while these have great success in killing and washing viruses from our hands, we need to consider how often and where to use them.
Undoubtedly, in the past several months, there’s been a steady stream of antibacterial and alcohol-based soaps being marketed to the general public. And while these have great success in killing and washing viruses from our hands, we need to consider how often and where to use them.
Should we be using antibacterial soaps for whole body cleansing? How often should we shower versus washing our hands? What’s the best way to avoid skin allergies, acne, or dry skin when choosing a cleansing routine? How clean is too clean? This article will address all of these questions and more.
Washing Our Hands in The Time of Coronavirus
We know that handwashing is the best prevention for the coronavirus. However, before the pandemic, many people weren’t educated about proper handwashing to prevent disease spread.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have always recommended regular handwashing for infection prevention. They provide researched education about how and when to wash our hands. The recommendations back in 2001 lightly supported the use of antibacterial soap. They cautioned that it may increase the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and negatively alter the skin flora (1,2).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have always recommended regular handwashing for infection prevention. They provide researched education about how and when to wash our hands. The recommendations back in 2001 lightly… Click To TweetIn 2020, the CDC now supports the use of soap and water as the gold standard for infection prevention and control. A search of CDC handwashing guidelines shows that they recommend only alcohol-based hand washing when soap and water aren’t possible (1,2).
As for antimicrobial soaps, the CDC no longer discusses using them at all. The reason is simple, antimicrobial soaps may do more harm than good.

What’s The Deal With Antimicrobial Soaps?
In recent years, several studies show that antimicrobial soaps may cause cracks and irritation to the skin. This creates more susceptibility to bacterial colonization. And as we know, the use of antimicrobial soaps may have a hand in creating superbugs that are resistant to antibiotics (2,3,4).
But unfortunately, antimicrobial soaps mess with our skin microbiome. Each area of the body has its own microbial balance, which maintains our health and prevents infection and disease. This balance can be disturbed by many factors which we are learning more about in modern times (3,5).
For example, in the book “The Whole Body Microbiome,” Dr. Brett Finlay and contributing scientists discuss microbiome balance issues in all areas of the body. With regard to the skin, they talk about how a simple problem like acne could be related to microbial imbalance on the surface of the skin (5).
For instance, a bacteria called Cutibacterium Acnes actually helps break down our oily skin secretions. This process creates an acidic environment that prevents the growth of Staphylococcus Aureus known for causing acne and other infections (5).
Who would have thought that one bacteria can prevent another worse bacteria from growing? But this is the case in almost all of our body microbiomes. Bacteria often compete and edge each other out, which keeps infections low and improves our well being. They also create enzymes and other by-products that contribute to the healthy function of our body (5,6,7).
For all these reasons, we don’t want to use antimicrobial soaps that kill off all the beneficial bacteria that are actually helping us.
 Why Should We Avoid Over-Cleaning Our Skin?
Why Should We Avoid Over-Cleaning Our Skin?
In the Whole Body Microbiome, the authors discuss research and studies showing one glaring truth. When it comes to the skin, less clean is better. Areas of the body such as hands, feet, genitals, and armpits should be washed daily with regular soap and water. But as for other areas like the face and rest of the body, it’s not necessary to scrub them daily (5).
Over-cleaning and using overly hot water can also damage our skin microbiome and cause more problems for our health. Many people don’t know that our skin and body microbiome plays a role in developing illnesses like asthma, eczema, autoimmune disease, and allergic reactions (5,7).
For instance, some studies show that eczema is related to higher levels of Staphylococcus Aureus. Without a balanced skin microbiome, these harmful bacteria are allowed to grow, causing the classic inflammatory skin lesions found in eczema (5,7).
Other studies show that exposure to beneficial skin microbes helps develop our immune system, thus preventing skin and systemic illnesses from developing later in life (5,6,8),.
Lastly, over-cleaning may cause cracks and open sores, which can increase infection risk. One study shows that damaged skin from over-cleaning is more likely to be colonized with several harmful microbes. Not only does this increase skin inflammation, but it may also perpetuate the spread of contagious infections (3,5).
So while it may be hard not to over-clean our hands during the pandemic, we can find a better balance for the rest of our body. Daily washing of feet, groin, hands, and armpits is good enough. But other parts of the body really don’t need to be over-cleaned.
For areas like the face, arms, legs, and hair, it seems the best skincare routine is to wash less frequently with plain soap and lukewarm water. This routine will also help prevent things like acne, wrinkles, dry skin, and other infections. Lastly, using a mild natural moisturizer can keep the skin supple without destroying the microbiome (1,2,5).

Conclusion
There’s never been a better time for more discussion and education around cleaning. Until now, most of us weren’t always sure how often we should wash our hands and clean our skin. With the push towards more frequent handwashing and the use of alcohol and antimicrobial soaps, it’s essential to learn what works and what doesn’t.
Frequent handwashing is critical in these trying times. And yes, we need to wash our dirtiest parts like feet, groin, and armpits. But surprisingly, we don’t need to over-clean other areas of our skin. And we should definitely stop the use of antimicrobial soaps. Pure soap and water is the best way to clean our hands and bodies.
Moreover, people may not understand how important our skin microbiome is for our health and wellbeing. Unfortunately, by over-cleaning and using hot water and antimicrobial soaps, we may be damaging our skin microbiome’s delicate balance. This has confirmed repercussions in the development of infections, allergies, and autoimmune diseases.
We also recommend learning about over-cleaning your home.
References
https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/7/2/70-0225_article
https://www.cdc.gov/handwashing/index.html
https://www.ajicjournal.org/article/S0196-6553(98)70025-2/fulltext
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/article-abstract/478930
https://www.wholebodymicrobiome.com
https://science.sciencemag.org/content/336/6080/489
https://www.jacionline.org/article/S0091-6749(13)01564-9/fulltext


 Side-Effects of Social Distancing & Home Isolation
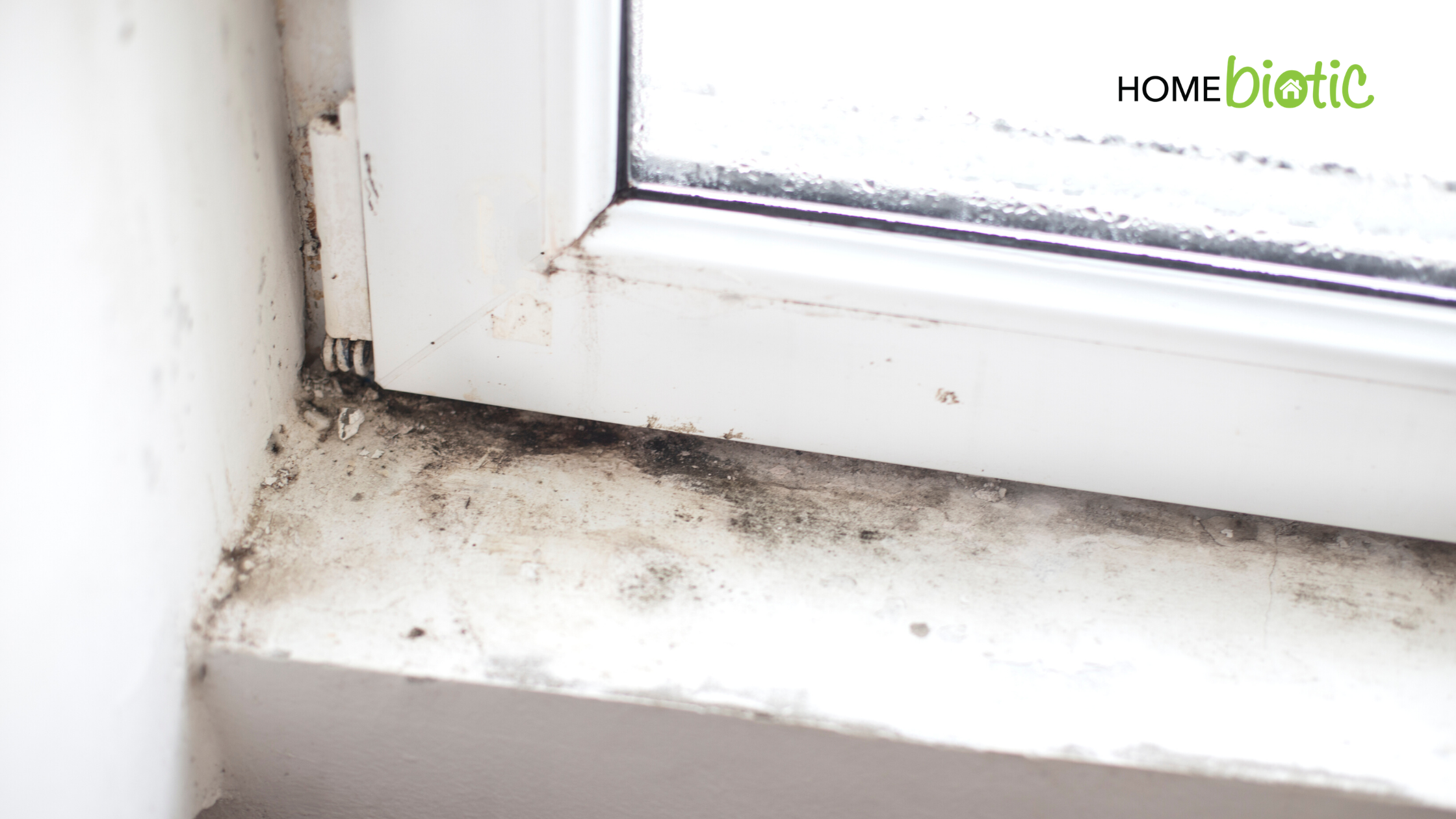
Side-Effects of Social Distancing & Home Isolation Why Do These Elements Cause Mold To Grow?
Why Do These Elements Cause Mold To Grow? How mold affects our health?
How mold affects our health?

 The Effects Of Mold On The Immune System
The Effects Of Mold On The Immune System Does Mold Make Us More Susceptible To Viruses?
Does Mold Make Us More Susceptible To Viruses?
