Mold Exposure and Lyme Disease: The Hidden Link
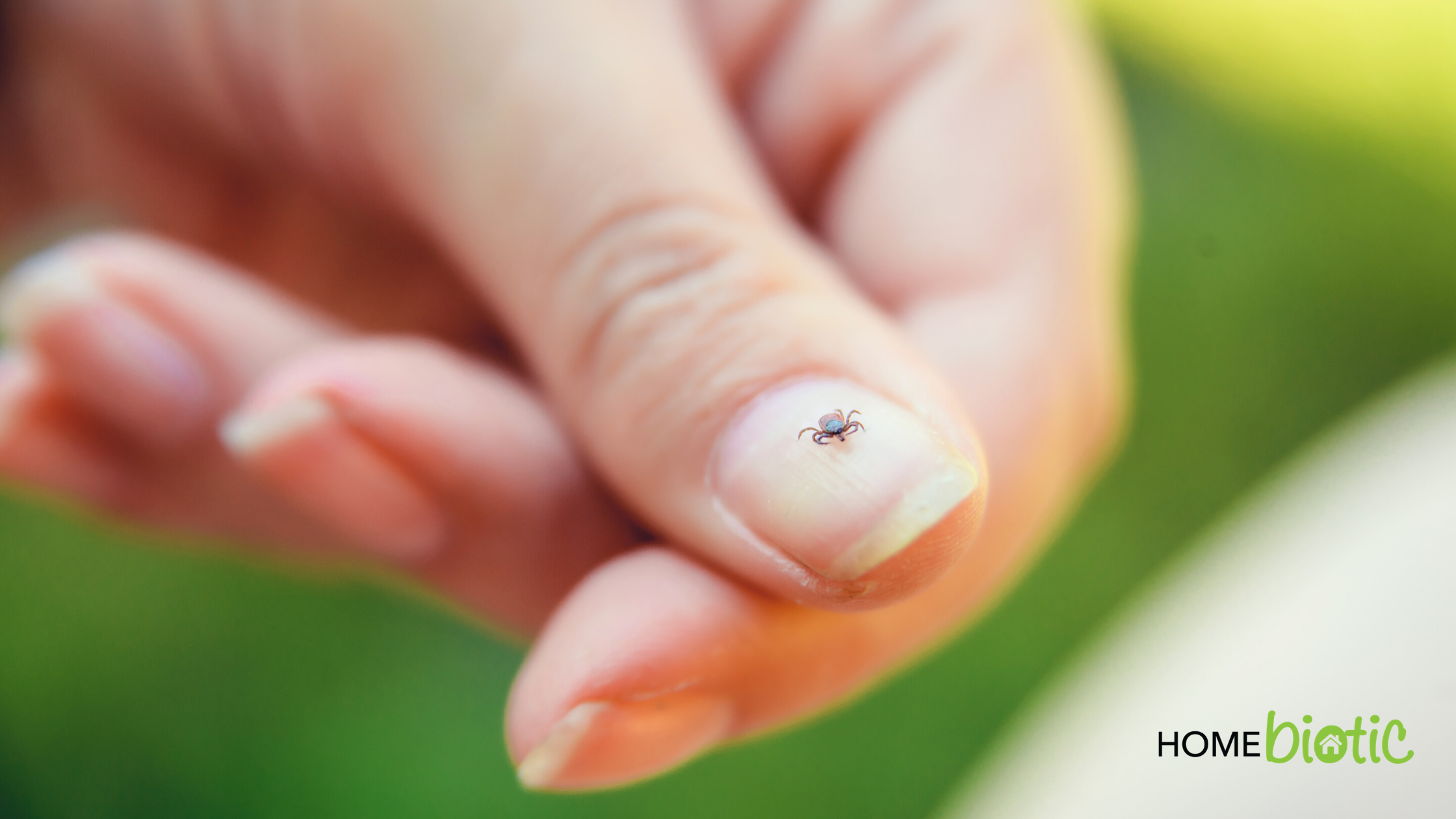

There is a clear connection between mold exposure and Lyme disease. Disruptions to your immune system resulting from exposure to mold can make you more likely to both contract Lyme disease and have medical complications with it. Beyond the typical precautions against tick bites, you can also help avoid it with simple household actions: Prevent mold exposure and Lyme disease risks are reduced.

May is National Lyme Disease month, which means that many clinicians, advocates, and researchers will be sharing facts to help increase awareness. Lyme disease affects approximately 30,000 Americans each year. Although it’s a highly treatable disease, it has a high potential to become chronic for many people 1. Also, Lyme disease often occurs in combination with other immune compromising conditions such as autoimmune disorders, allergies, celiac disease, Epstein Barr virus, and other infections 2.
However, did you know that mold toxicity is also an important issue for people with Lyme disease? Unfortunately, the immune-compromising effects of mold toxicity can make you more susceptible to contracting Lyme disease. Also, once infected with the Lyme bacteria, mold illness can make you more likely to have chronic issues with Lyme disease.
 How Mold Affects the Immune System
How Mold Affects the Immune System
The most common household mold species are Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Cladosporium. But there are thousands of other different kinds of mold species. Although many of them are not harmful in most situations, some can cause serious illness 3. The problem with certain mold species is that they produce substances called mycotoxins which are harmful to human health.
The symptoms of mold illness range from mild to severe depending on the health status, immune system, and genetic factors of different people.
At the very least, the effects of mycotoxins on human tissues can cause mild allergic symptoms. But sometimes it can lead to more severe respiratory or other systemic problems that can cause chronic illness and even death 3,4,5. The main problem with mold and human health is that it causes severe disruptions in the immune system resulting in either an over-reaction or under-reaction 6.
The main problem with mold and human health is that it causes severe disruptions in the immune system resulting in either an over-reaction or under-reaction Share on XWhat this means is that mold may be a factor in the development of autoimmune issues as well as immune-deficiency problems. Either of these conditions can make it difficult for a human body to deal with other infections, such as Lyme disease 4,5,6.
Several studies have shown that people living in damp and moldy environments are more prone to inflammatory illnesses or infections that result from immune deficiency. This is especially true if their living environments lack surrounding biodiversity that is void of other helpful microbes 5,6,7,8,9. This is the reason why people with mysterious inflammatory issues and other chronic health problems often test with high levels of mycotoxins.
Further tests often reveal other infections such as Lyme disease. This is no coincidence. Instead, it reveals immune systems that are unable to cope, and mold toxicity may be a massive piece of the puzzle.
 How Lyme Disease Affects the Human Body
How Lyme Disease Affects the Human Body
Lyme disease is caused by a spirochete bacteria that is transmitted through tick bites. A tick needs to be attached to the human body for at least 24 hours to transmit the disease. This is why most health education is aimed at early prevention by instructing people how to quickly and adequately remove a tick 1,2. The problem is that many people are under the impression that they can prevent Lyme disease since a tick is easy to find. Tick bites are relatively irritating to the skin. Also, the tick swells, which may make it easy to detect. Therefore, people feel that they can remove it before 24 hours are up.
Unfortunately, most people don’t remove ticks properly. Instead, they pull it out and leave the mouthparts behind. The problem is that those mouthparts stay embedded in the skin where they can continue to transmit the Lyme spirochete 1,2.
Lyme disease initially causes fever, skin rash, joint pain, muscle pain, and headaches. If treated rapidly, a person can make a full recovery. However, Lyme disease has been known to turn chronic, especially if early treatment wasn’t initiated. And even with early treatment, many people still go on to develop chronic Lyme disease symptoms 1,2,10.
Lyme disease initially causes fever, skin rash, joint pain, muscle pain, and headaches. If treated rapidly, a person can make a full recovery. However, Lyme disease has been known to turn chronic, especially if early treatment wasn't… Share on XWhat’s interesting is that chronic Lyme disease symptoms are very similar to the signs of mold toxicity. Also, chronic Lyme symptoms are similar to many diseases of the immune system. When this occurs, the clinical picture can become confusing to both the patient and doctors 4,10,11. Symptoms of chronic Lyme disease range from digestive issues, neurological problems, heart damage, and severe musculoskeletal pain 1,2.
Indeed, many people who present with multiple and chronic health issues are often investigated for co-morbid and related conditions such as mold illness and Lyme disease.
 The Connection Between Mold & Lyme Disease
The Connection Between Mold & Lyme Disease
As discussed above, the main problem with mold is that it renders our immune system less capable of coping with other infections. Indeed, many people exposed to tick bites don’t actually get sick. And if they do, the illness is short-lived and doesn’t turn chronic.
However, the problem lies when a person gets bit by a Lyme infected tick, and their immune system is already preoccupied with fighting off mold toxicity. Unfortunately, they may be unable to fight off this new infection 11,12,13,14.
Also, even with antibiotic treatment, an immunocompromised host may still go on to develop chronic Lyme-related health issues.
Many people with co-occurring Lyme and mold issues develop something called Chronic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (CIRS). This syndrome is difficult to treat and can wreak havoc on the health, finances, and quality of life of those affected. Furthermore, people with Lyme disease are less likely to clear toxins from their bodies. Likewise, mold toxicity makes Lyme disease treatment less likely to work. Thus it becomes a vicious cycle causing crippling symptoms that are difficult to treat 11,12,13,14.
Many people with co-occurring Lyme and mold issues develop something called Chronic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (CIRS). This syndrome is difficult to treat and can wreak havoc on the health, finances, and quality of life of those… Share on XConclusion
Since these two conditions create a perfect storm for inflammatory illness, the obvious solution is to work on both prevention and proper diagnosis for both. Preventing mold illness by properly cleaning and treating moldy environments is paramount. By doing so, the people living in those environments will maintain a healthy immune system. And as we know, a healthy and balanced immune system can fight off other infections like Lyme disease.
Preventing mold illness by properly cleaning and treating moldy environments is paramount. By doing so, the people living in those environments will maintain a healthy immune system. And as we know, a healthy and balanced immune system… Share on XHowever, many people don’t even know they have mold illness until they become sick with Lyme disease, which then becomes chronic. Often, it takes a long time with much frustration before a person learns that they’re actually dealing with two chronic illnesses that are exacerbating each other. Since we know that mold illness increases susceptibility to other infections, it makes sense to raise awareness so that people can take action to prevent mold now.

By taking steps to decrease mold problems, people will have a more robust immune system, which will prevent chronic Lyme disease from taking hold. More so, a stronger immune system means fewer chances of developing Lyme disease in the first place.
REFERENCES
1. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance/index.html
2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3542482/
3. https://www.cdc.gov/mold/faqs.htm
4. https://www.prohealth.com/library/overview-lyme-disease-mold-illness-91639
5. https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0017/43325/E92645.pdf
6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5377931/
7. https://robdunnlab.com/science-portfolio/never-home-alone/
8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5108756/
9. https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Arch+Environ+Health&title=Mixed+mold+mycotoxicosis:+immunological+changes+in+humans+following+exposure+in+water-damaged+buildings&author=MR+Gray&author=JD+Thrasher&author=R+Crago&author=RA+Madison&author=L+Arnold&volume=58&publication_year=2003&pages=410-20&pmid=15143854&
10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5986024/
11. https://www.gordonmedical.com/unravelling-complex-chronic-illness/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Townsend-Letter-Mold-Article-1.pdf
12. https://www.betterhealthguy.com/topics/mold
13. https://drjaydavidson.com/toxic-mold-lyme/
14. https://www.lymecompass.net/mold-intolerence.html


 In the past decade, the importance of a healthy gut biome has been discussed between scientists, medical professionals, and health consumers. By now, most people know that bacteria reside in our guts and that they’re essential to our health. These bacteria are, together, what create the biome. However, many people still don’t understand why having diverse bacteria is important. More importantly, most people don’t understand the similarities and relationship between our home biome and the gut biome. We need the biome in our guts and our homes to be healthy and diverse at the same time.
In the past decade, the importance of a healthy gut biome has been discussed between scientists, medical professionals, and health consumers. By now, most people know that bacteria reside in our guts and that they’re essential to our health. These bacteria are, together, what create the biome. However, many people still don’t understand why having diverse bacteria is important. More importantly, most people don’t understand the similarities and relationship between our home biome and the gut biome. We need the biome in our guts and our homes to be healthy and diverse at the same time. What is The Gut Biome?
What is The Gut Biome? What is The Home Biome?
What is The Home Biome? How Are The Gut & Home Biome Related?
How Are The Gut & Home Biome Related?


 HOW DOES THE “FARM EFFECT” WORK?
HOW DOES THE “FARM EFFECT” WORK? WHY DO I WANT TO REPLICATE THE “FARM EFFECT” IN MY HOME?
WHY DO I WANT TO REPLICATE THE “FARM EFFECT” IN MY HOME?
 Next, we need to bring in more soil-based microbes, and there are a few ways that are not only fun but easy.
Next, we need to bring in more soil-based microbes, and there are a few ways that are not only fun but easy.